What is cuprite? what is cuprite used for? Is cuprite toxic?
What is cuprite? what is cuprite used for? Is cuprite toxic?
Blog Article
What is cuprite?
Cuprite is a copper-containing oxide mineral and an ore that oxidizes copper. Cuprite is mainly related to the oxidation of copper ore in the oxidation zone. Copper minerals are transformed into cuprite under the action of oxidants, water and air. Cuprite has certain economic value. Although the copper content is lower than that of chalcopyrite, it is also one of the main sources of copper extraction.

Properties of cuprite
Chemical properties of cuprite: The chemical formula is Cu₂O, which is mainly composed of 88.8% copper and 11.2% oxygen. It is insoluble in water, but soluble in acid and ammonia. It is relatively stable under normal circumstances, but may be oxidized in a humid environment.
Physical properties of cuprite: It usually appears red, dark red or reddish brown. It has a metallic to semi-metallic luster and a smooth and bright surface. The hardness is low, between 3.5-4, but the density is high, 6.1g/cm³. It is usually cube, octahedron, dodecahedron, with a flat surface and symmetrical shape.
Other properties: Cuprite is non-magnetic and opaque, but has good conductivity. It is also a semiconductor material, mainly used to make electronic devices and solar cells.

Cuprite crystal form
Cube: One of the common crystal forms of cuprite, with smooth square or rectangular faces on the surface.
Octahedron: Crystals of this form are usually symmetrical octahedrons with beautiful appearance.
Dodecahedron: Cuprite may also form dodecahedron crystals with sharp edges in some cases.

What is the chemical formula of cuprite?
The chemical formula of cuprite is Cu₂O, which means it consists of two copper atoms and one oxygen atom. This is a copper oxide, also known as cuprous oxide.
Is cuprite toxic?
Cuprite is a natural copper ore that is not toxic in itself. However, during the mining, processing or handling of cuprite, the dust produced will irritate the respiratory tract, and long-term inhalation will affect health. Under normal circumstances, the copper in cuprite is relatively stable, but excessive intake of copper compounds may lead to poisoning, with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. If cuprite is not handled properly, copper ions may enter the environment, pollute water sources and soil, and affect the ecological balance. It is very important to take protective measures.

What are the uses of cuprite?
Smelting: Cuprite has a high copper content and is one of the raw materials for refining metallic copper. It is widely used in construction, electrical and manufacturing industries.
Decoration: Cuprite has a beautiful red appearance and is often used as a mineral specimen, collection and decoration. It also has a unique crystal form and is popular among mineral enthusiasts and collectors.
Electronics: Cuprite has semiconductor properties and is often used to make solar cells and electronic devices.
Pigments: Because of its unique red color, it is often used as a pigment in ceramics, glass and paint.
Chemical industry: In the chemical industry, cuprite can promote some chemical reactions and act as a catalyst.
Scientific research: The copper in cuprite exists in an oxidized state and is a research material in metallurgy, geology and mineralogy. Scientists obtain more knowledge about copper minerals by studying the composition, structure and extraction methods of cuprite.

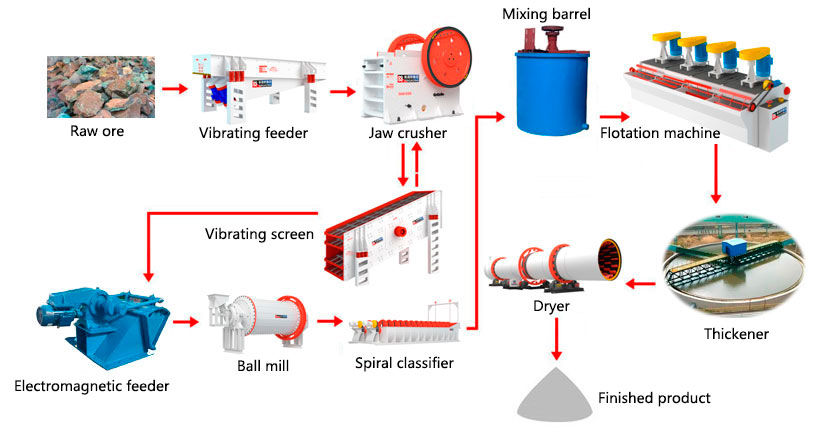
Cuprite flotation process
Ore preparation: Cuprite needs to be crushed and screened. Use jaw crushers or cone crushers to crush large pieces of ore into small particles, and then use screening equipment such as circular vibrating screens to screen out ore particles that meet the requirements.
Grinding and grading: The crushed material is sent to the ball mill for grinding to reach the flotation particle size. Then it is graded by a spiral classifier, and those that do not meet the requirements are sent back to the ball mill for grinding.
Reagent preparation: Before flotation, it is necessary to prepare an appropriate amount of flotation reagents such as collectors, frothers and inhibitors.
Flotation process: It is divided into three steps: roughing, scavenging and concentrating.
Flotation process type: According to different ore properties and mineral processing requirements, it can be divided into mixed flotation process, preferential flotation process, positive flotation process and reverse flotation process.
Concentrate and tailings treatment: The concentrate flotated is further processed to extract copper elements. The tailings after flotation should be properly handled to avoid environmental pollution.
Author:[Xingaonai]
Article Title: What is cuprite? what is cuprite used for? Is cuprite toxic?
Reprint URL: https://www.xgncrusher.com/Industralnews/what-is-cuprite-uses-is-it-cuprite-toxic.html